Why Are Brass Standoffs the Secret to Project Success?
- Blog
- Why Are Brass Standoffs the Secret to Project Success?

- June 25, 2023 by Admin
- Brass Standoff & Spacers
Why Are Brass Standoffs the Secret to Project Success?
Introduction:
Miniature components are important in electronics and mechanical engineering, contributing to your projects’ functionality, reliability, and success.
These discreet but important elements include brass standoffs that play an important role in a variety of applications.
With threaded ends, these cylindrical pillars provide stability, proper spacing, and electrical insulation, making them an invaluable addition to your DIY tool kit.
In this blog post, we dive into the world of brass standoffs and explore their properties, uses, and why they are essential for a variety of projects
Understanding Brass Standoffs:
Brass standoffs, also known as threaded standoffs or pillars, are small cylindrical devices made primarily of brass.
Their defining feature is the threaded ends, facilitating easy installation and secure fastening.
The spacer body can be unthreaded, internally threaded, externally threaded, or double-threaded, depending on the application.
Brass is an ideal material choice due to its outstanding electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength.
However, these spacers are also available in Stainless steel (SS), Mild steel (MS), and Aluminum.
Versatile Applications:
Brass standoffs find wide-ranging applications across numerous fields, including electronics, telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and DIY projects.
Let’s explore some of their common uses:
a. PCB Mounting:
Standoffs provide vital support and spacing for printed circuit boards (PCBs). By elevating the board, they prevent direct contact with the mounting surface, reducing the risk of short circuits.
Standoffs also aid in aligning and securing the PCB within an enclosure.
b. Component Mounting:
Brass standoffs ensure proper alignment and spacing when assembling electronic components or modules.
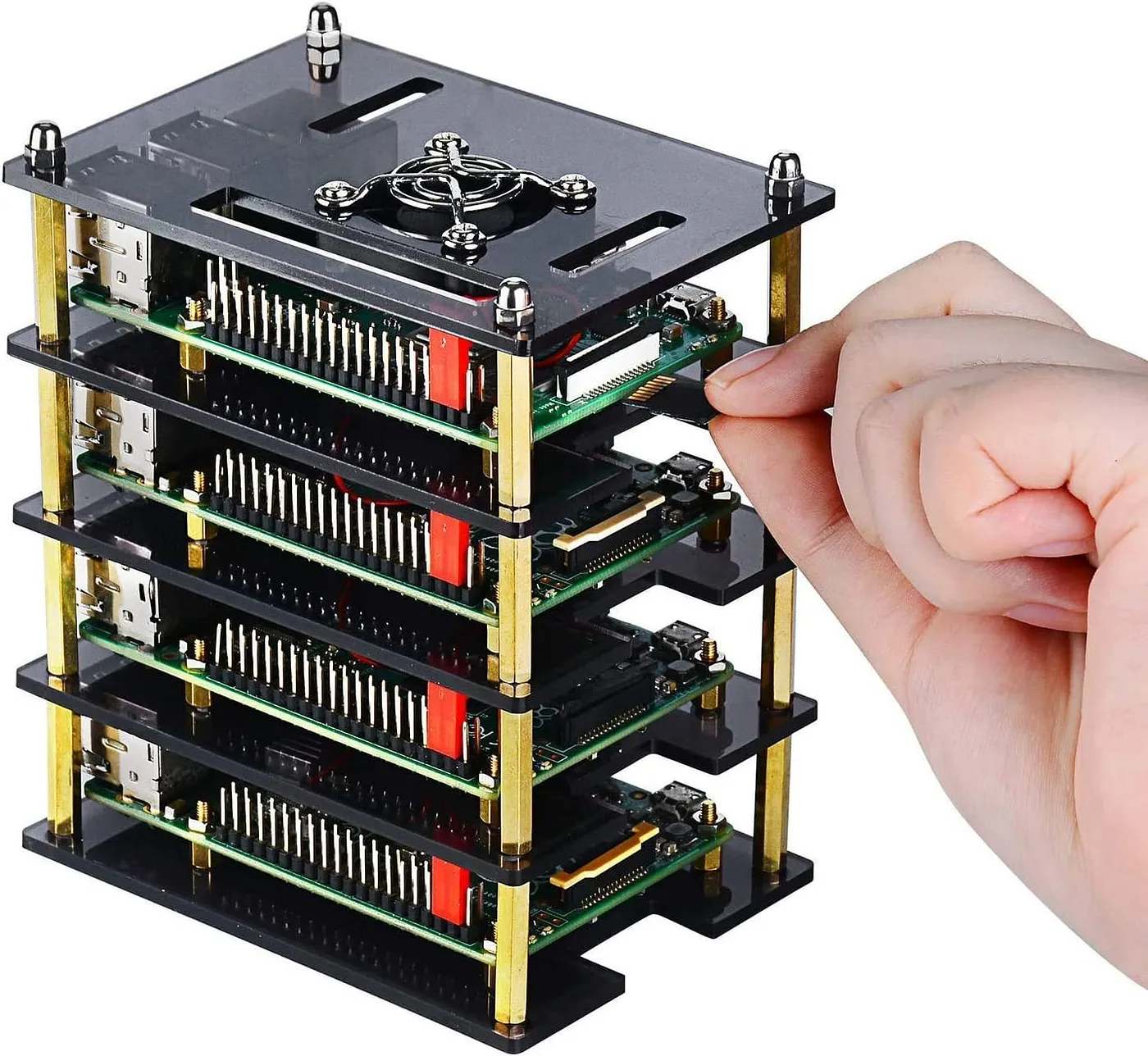
They create a robust structure, enabling organized cable routing, reducing strain on delicate connections, and facilitating efficient cooling through adequate airflow.
c. Panel Mounting:
Standoffs are instrumental in mounting panels, displays, and screens onto enclosures or housings.
They maintain a consistent distance between the mounted object and the surface, simplifying maintenance, repair, or replacement tasks.
d. Custom Enclosures:
DIY enthusiasts often employ brass standoffs to construct custom enclosures for their projects.
These standoffs enable the secure attachment of various components such as Raspberry Pi boards, Arduino modules, and other electronics within the enclosure.
e. Mechanical Engineering:
Brass standoffs assist in joining multiple parts or assemblies in mechanical applications, providing stability, spacing, and isolation.
They are commonly utilized in robotics, industrial machinery, and equipment assembly.
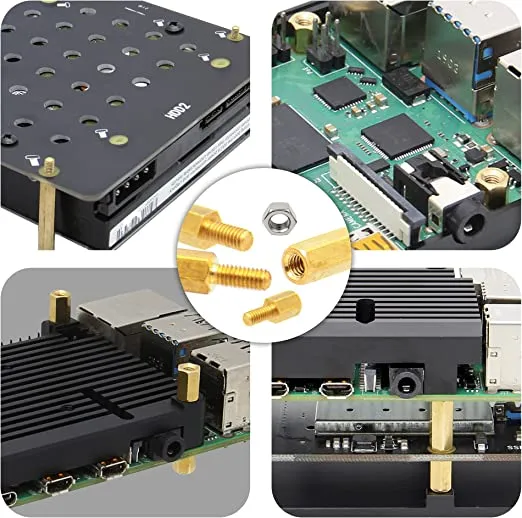
Benefits of Brass Standoffs:
Brass standoffs have many advantages that make them the preferred choice for many projects.
A. Electrical insulation:
Brass is a good conductor, but standoffs provide electrical isolation between components.
This feature is important in applications where different voltage levels or signals need to be separated to prevent interference.
B. Increased Mechanical Stability:
Standoffs create a stable structure to ensure secure assembly and correct component alignment, reducing the risk of damage from vibration, shock, or accidental impact.
C. Easy Installation:
The threaded ends of the brass standoffs allow for easy and quick installation.
It can be easily tightened by hand or with a simple tool such as a screwdriver.
D. Corrosion Resistance:
Brass’s natural corrosion resistance makes it suitable for applications where moisture and environmental factors are a concern.
Choosing the Right Brass Standoff:
Selecting the appropriate standoff depends on various factors, including the required length, thread size, and the need for an unthreaded or threaded body.
It is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose standoffs that meet those needs.
Choosing the proper spacers is crucial for precision engineering and creating robust structures.
Brass spacers offer exceptional versatility and functionality in a wide range of applications.
Various Types of Brass Spacers:
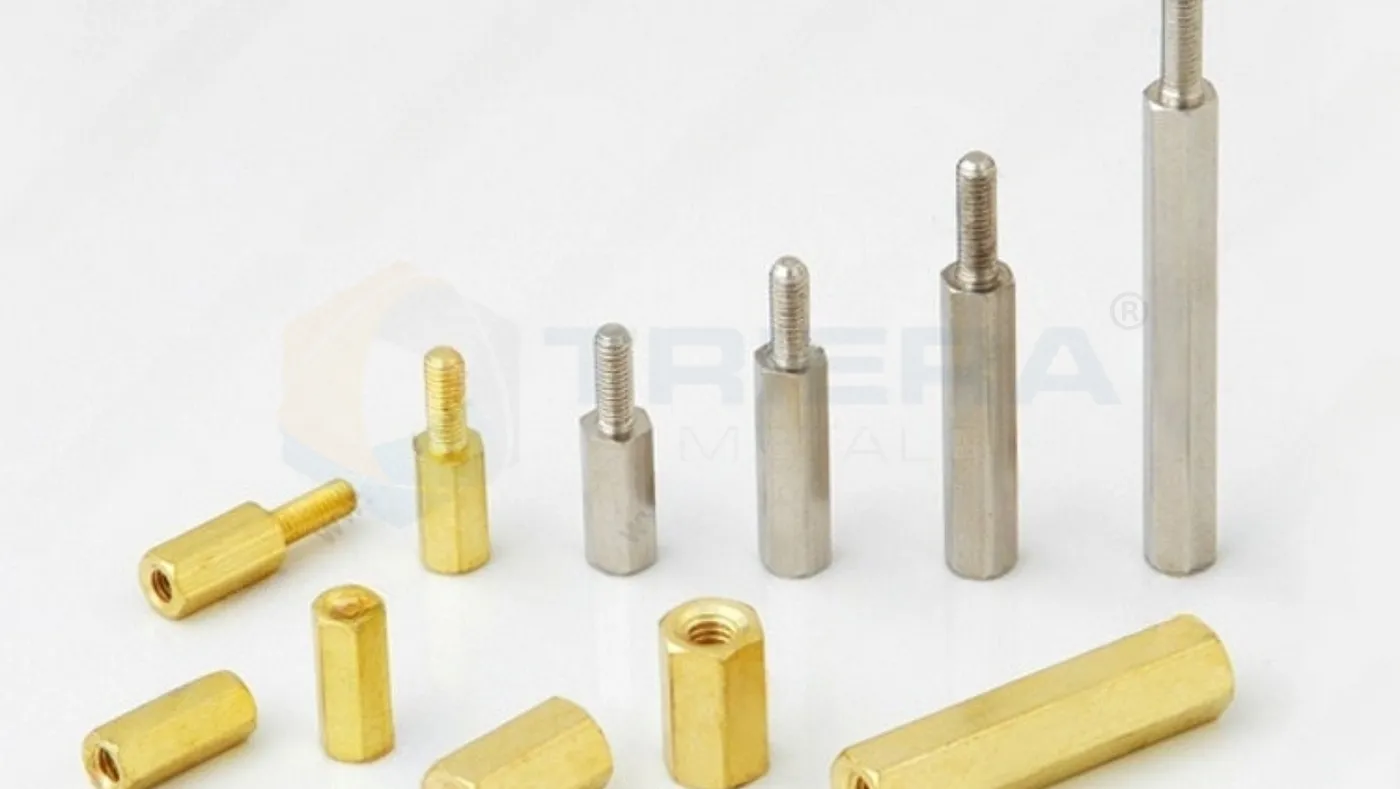

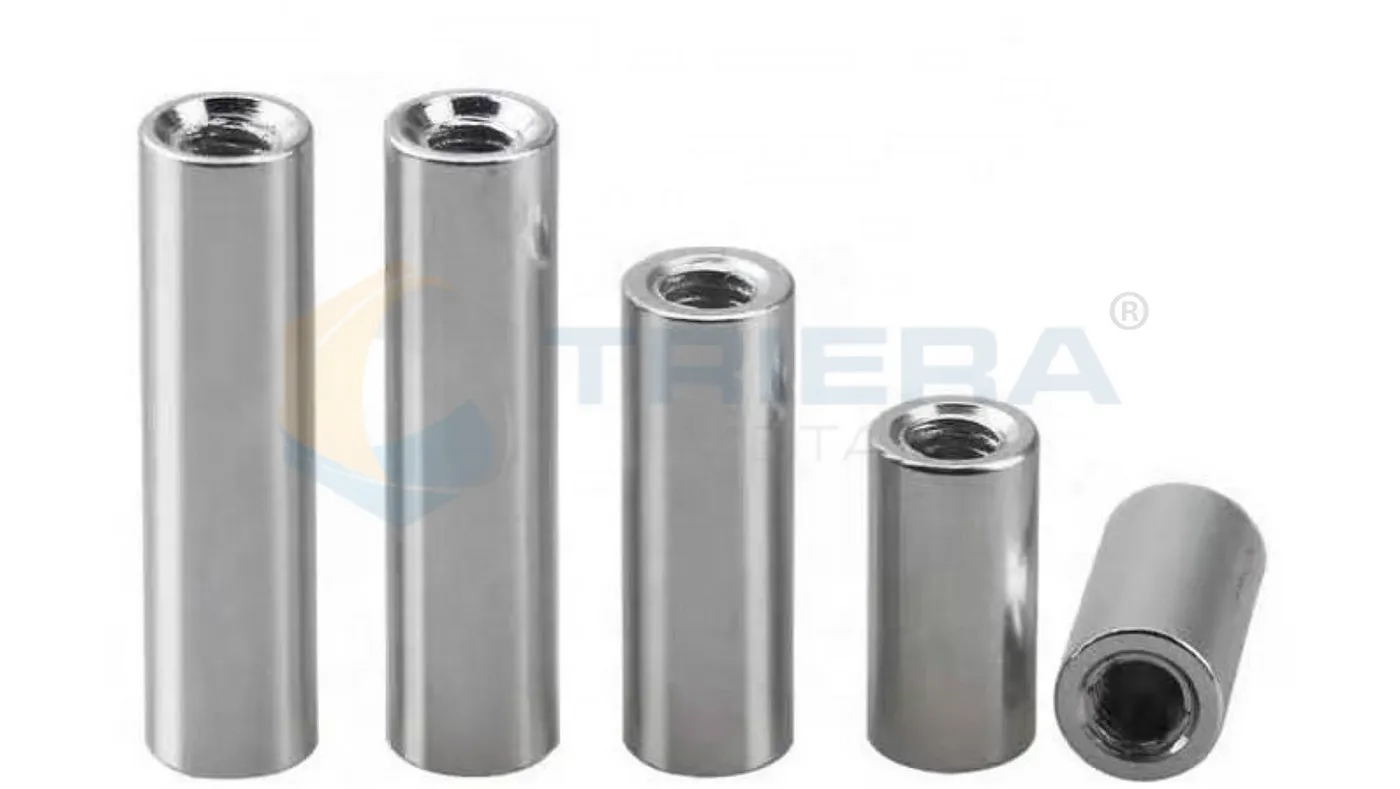
Round Spacers
Cylindrical shape with consistent diameter throughout length.
Commonly used for PCB mounting, component stacking, and general applications where reliable spacing and alignment are crucial.

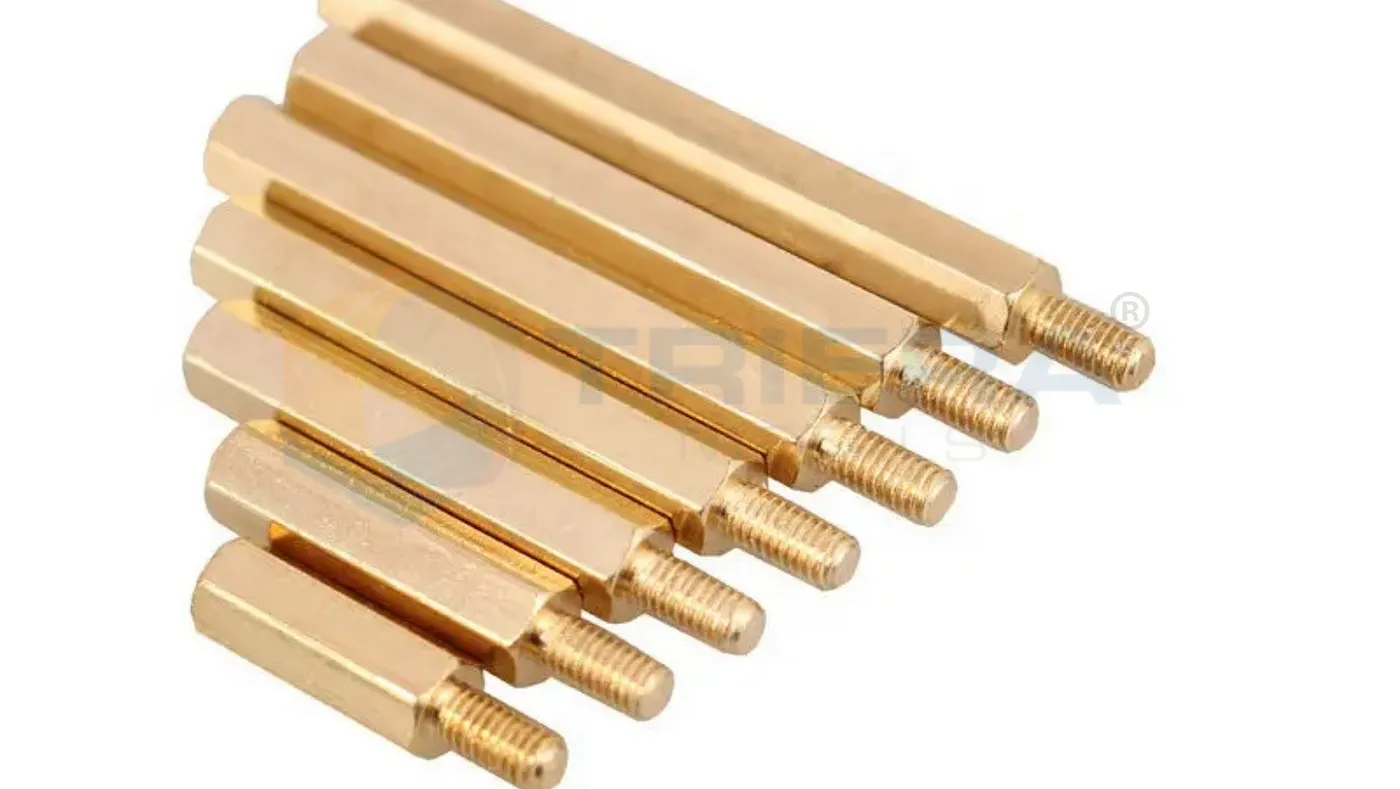
Hexagonal Spacers
Hexagon-shaped body with a flat surface on each of the six sides.
Often preferred in applications where secure fastening and torque control are essential.

Swage Spacers
Knurled body with grooves or serrations that grip surrounding material.
Eliminates the need for additional fasteners or adhesives, providing a reliable and secure attachment.
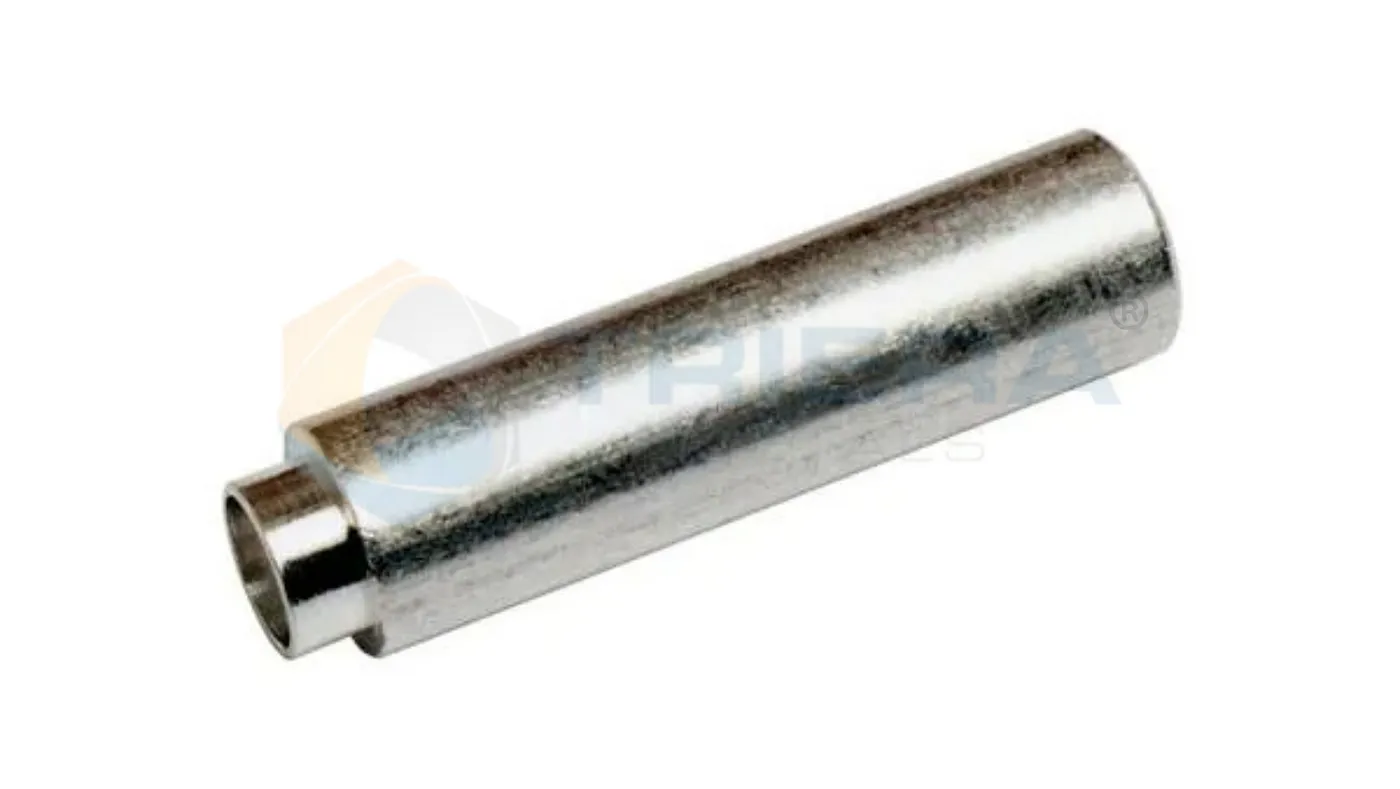

Male-Female Standoffs
Consists of two parts — a male end with external threads, and a female end with internal threads.
Used to create a connection between two components or surfaces while maintaining a specific distance between them.
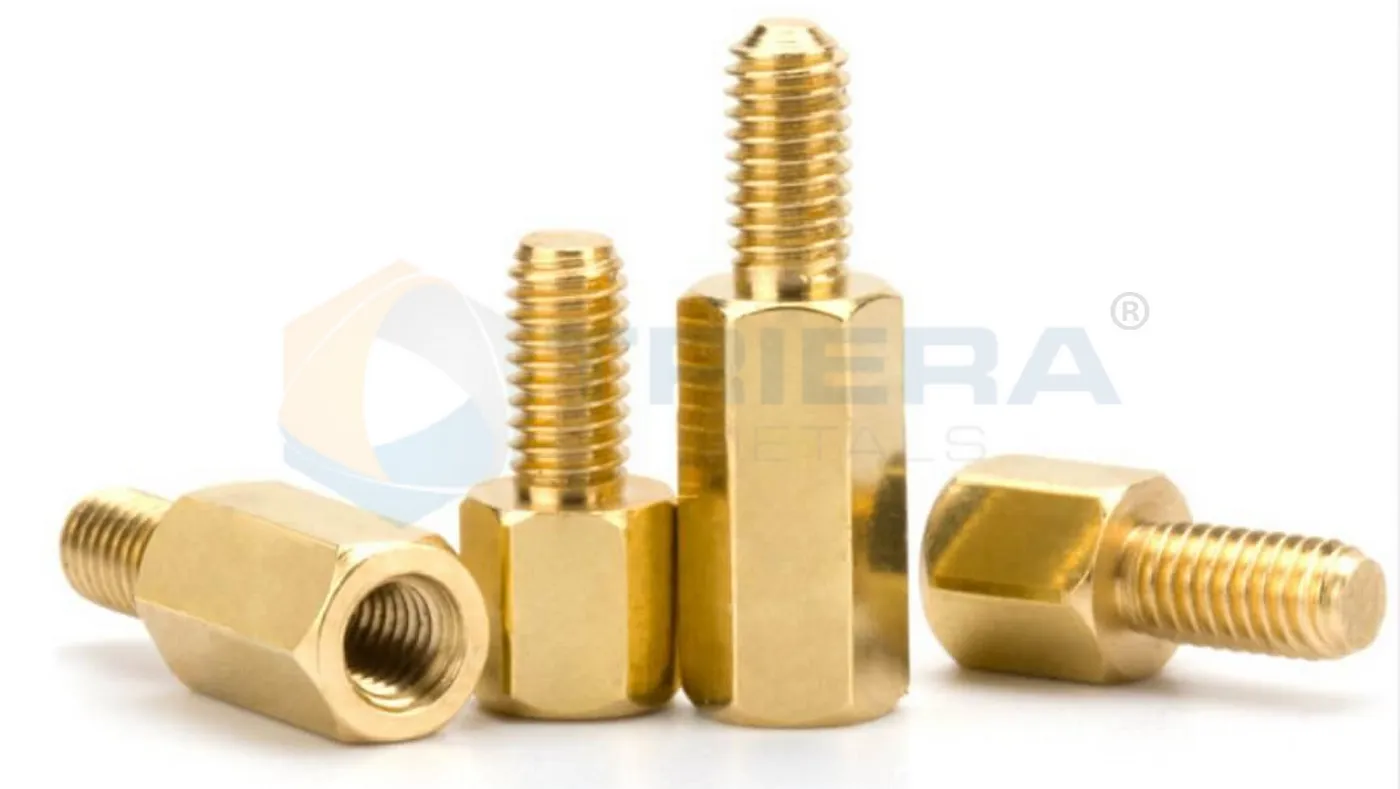

Male-Male Standoffs
They have male threads on both ends.
These standoffs create a fixed distance between two surfaces.
They are used for fastening those surfaces together.
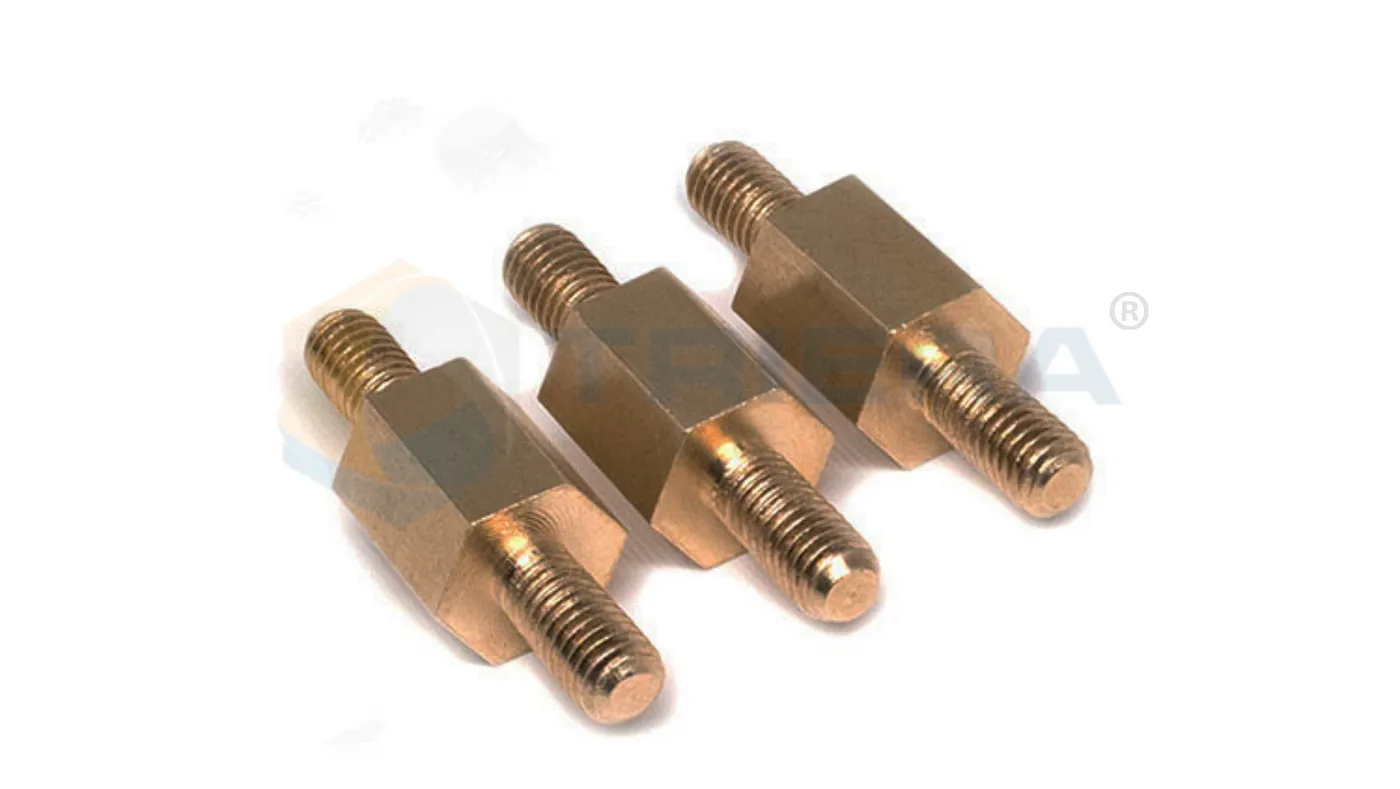

Female Standoffs
They have male threads on both ends.
These standoffs create a fixed distance between two surfaces.
hey are used for fastening those surfaces together.
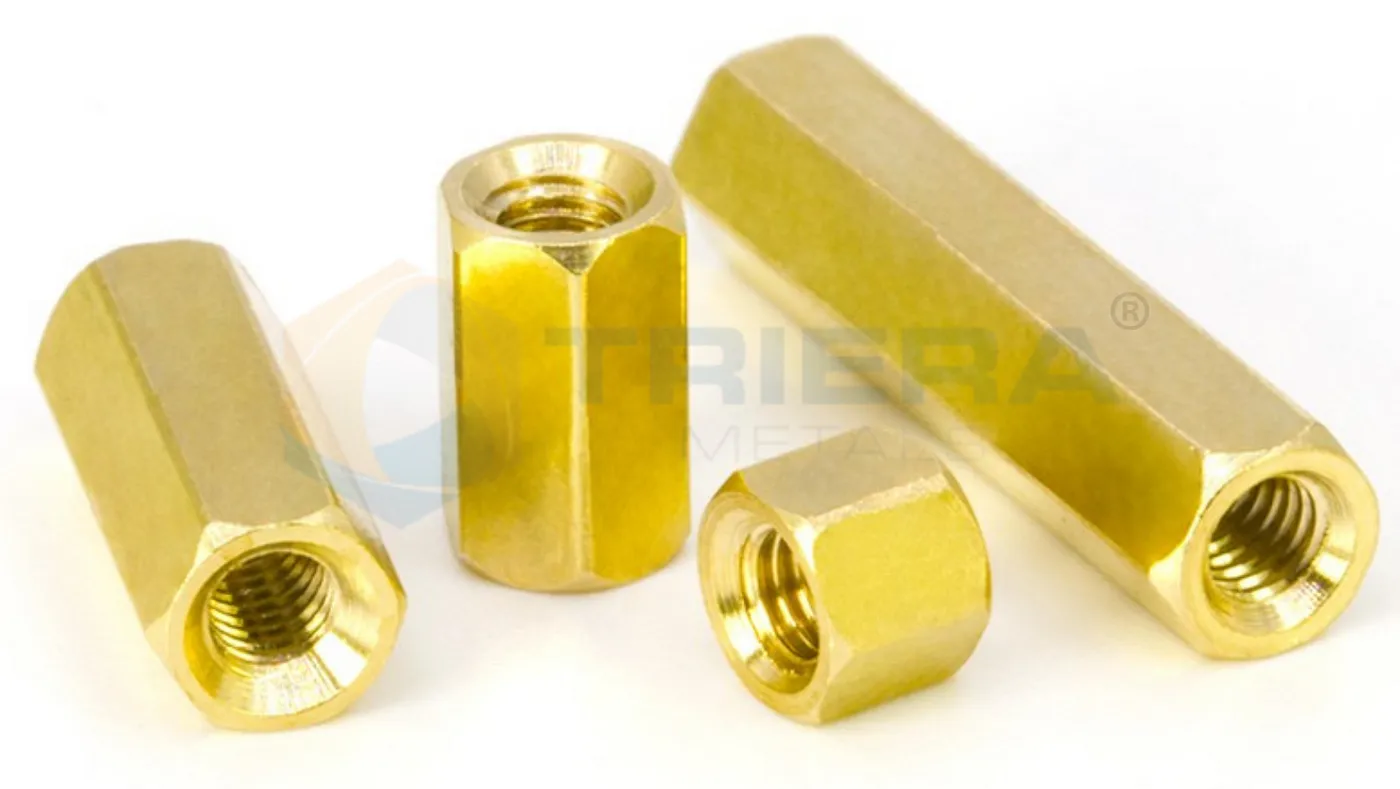

Knurled Standoffs/Spacers
Knurled spacers have a knurled texture on the outer surface.
They are used to create a fixed distance between components.
The knurled texture provides a secure grip for easy handling and adjustment.

Swivel Spacers
Swiveling or rotating feature at one end, allowing for easy angular adjustment.
Ideal for applications where alignment precision is crucial.
Conclusion:
Although small in size, brass standoffs play a significant role in ensuring project stability and functionality.
Whether you’re assembling electronic components, mounting PCBs, or creating custom enclosures, these unassuming pillars are indispensable.
With their electrical isolation, mechanical stability, and versatility, brass standoffs have rightfully earned their place as a vital component in the realms of engineering and DIY projects.
So, the next time you embark on a project, remember the power of brass standoffs — they might just be the missing piece you need for success.
If you are looking for a quality Standoff manufacturer visit us at: www.trierametals.com

